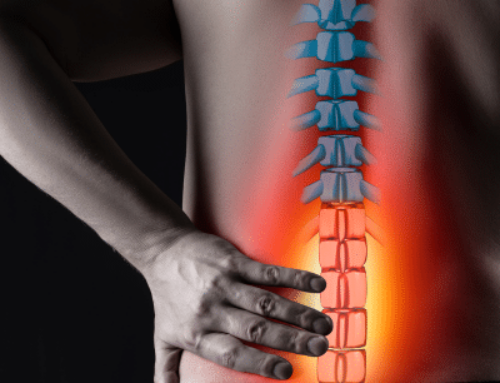
Despite its name, degenerative disc disease is not really a “disease” at all. More accurately, it’s a condition caused by damage to one or more of your spinal discs.
Despite its name, degenerative disc disease is not really a “disease” at all. More accurately, it’s a condition caused by damage to one or more of your spinal discs.
As you age, the discs in your back lose water and lose their height; but a newborn’s discs are composed of 80 percent water. Wear and tear, poor posture and incorrect movements can also cause disc deterioration.
Discs function as shock absorbers between the bones in your spine. This loss of water brings them closer together, and the nerve openings in your spine become narrower as a result. Because of these age-related changes, discs tend not to absorb shocks as well as they formerly did — and we feel this when we walk, run and jump.
Unlike other tissues in the body, there is very little blood supply to the discs. Once deterioration in your discs occurs, they lack the ability to repair themselves; and degeneration sets in.
What Are the Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease?
- Back and/or leg pain that is often worse when sitting
- Pain that worsens when bending, twisting or lifting things
- Tingling or numbness in the back, buttock area or in the extremities
- Difficulty standing still for long periods of time
- Pain that eases a bit when changing positions or lying down
- Periods of severe pain that can last anywhere from a few days to months
- Depending on where the disc is located in the spine, pain affecting the lower back, buttocks and thighs; or pain affecting the neck and radiating down the arms
- Leg weakness
Diagnosing Degenerative Discs
Our pain specialists will physically examine your back and lower extremities. We will be checking for things like flexibility, range of motion and certain signs that indicate nerves in your back are being affected. This usually includes testing your muscle strength and your reflexes. We may also order X-rays or an MRI scan.
Treatment Options
No one-size-fits-all treatment for degenerative disc disease exists. Treatment options depend on the severity of your symptoms, as well as the extent to which they limit or disrupt your daily activities. Possible nonsurgical treatments include, but are not limited to:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Nerve block
- Steroid injections
At Hampton Roads Orthopaedics Spine & Sports Medicine, we always begin with the least-invasive treatments before any surgery is recommended. Pain is subjective — experienced differently by each patient — and although most people aged 60 and over have some degree of degenerative disc disease, not all of them experience debilitating pain. Please contact us at (757) 873-1554 to schedule an appointment with one of our pain management specialists.